Data communication
 |
| Data Communication Components(Image Source: Data Communication and Networking By Behrouz A. Forouzan) |
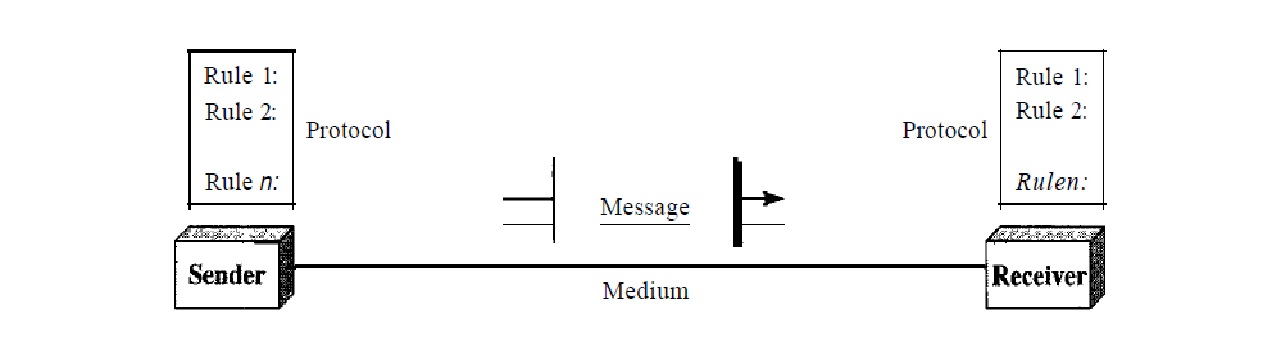
Data communication is the exchange of information between computers. Data communication is used to send and receive data. Email, Instant Messaging, Phone calls, electronic meetings and video conferencing are applications of data communication. Data communication involves both hardware and software. Data communication consists of five elements. Sender, Receiver, Message, transmission medium and protocol.
SENDER
The sender is the device or computer that
sends data.
RECEIVER
The receiver is the device or computer which
receives data from the sender.
MESSAGE
The message is data which user wants to send
or receive. Data can be any format such as text, numbers image, and video.
TRANSMISSION
MEDIUM
The transmission medium is the physical path which
is used to send message between sender and receivers. The transmission medium
plays an important role in data communication effectiveness. Fiber optic cable,
coaxial cable, twisted pair cable, infrared and radio waves are types of the transmission
medium.
PROTOCOL
A protocol is an agreement
between two computers. It is sets of rules to be followed by both computers for
data communication. If Computer A wants to communicate with Computer B then
both have to follow some protocols. Let us understand the protocol by a general
example, John wants to communicate with Shahzad. John is from the United States
of America(USA) knows English and Shahzad from Pakistan know Urdu, so for
communication, they developed a protocol that they will always talk in English
so that they can communicate and understand each other. Same for computers,
Computer A wants to communicate with Computer B, he will communicate with
certain protocols.
Data
communication performance depends on certain characteristics. An effective data
communication system must have four characteristics, which are explained below.
1.
DELIVERY:
A sender that sends
data to a specific computer must be delivered to that computer and no other
computer would receive that data.
2.
ACCURACY
The computer must
deliver data that should be accurate it should not be altered or changed during
data transmission. The altered data is not usable and will affect the data
communication system performance.
3.
TIMELINESS
The computer must
deliver data at a certain time. The data which receives data late will be not useful.
For example, in a video conferencing system if video is delivering after big
delay then this application will be useless.
4.
JITTER
Data communication
sends data in packets. If these packets will not be delivered by the communication
system in order or there is a variation in arrival time then the message will
be useless and the receiver will get the distorted or wrong message.
Tags: Data Communication, Computer Networks




